Quantifiers are words that are used to state quantity or amount of something without stating the actually number.
Quantifiers are words that tell us how much or many of something we have.

- There many flowers.
- Most of the students were in the University.
- Fatima owns a few books.
- She doesn´t have enough money.
- My mother have a plenty house.
- She doesn´t have many oranges.
- I know a little about the American Culture.
- They have many cars in their house.

1. How many apples do you have?
2. How much sugar do you need?
3. You have too many works.
4. You have too much grape juice.
5. She have enough textbooks.
6. He have enough soda.
7. They have a few cars.
8. Pablo drink a little Vodka.
MORE INFORMATION
SHORTCUT
THE PARTS OF THE SPEECH
TYPES OF SENTENCES
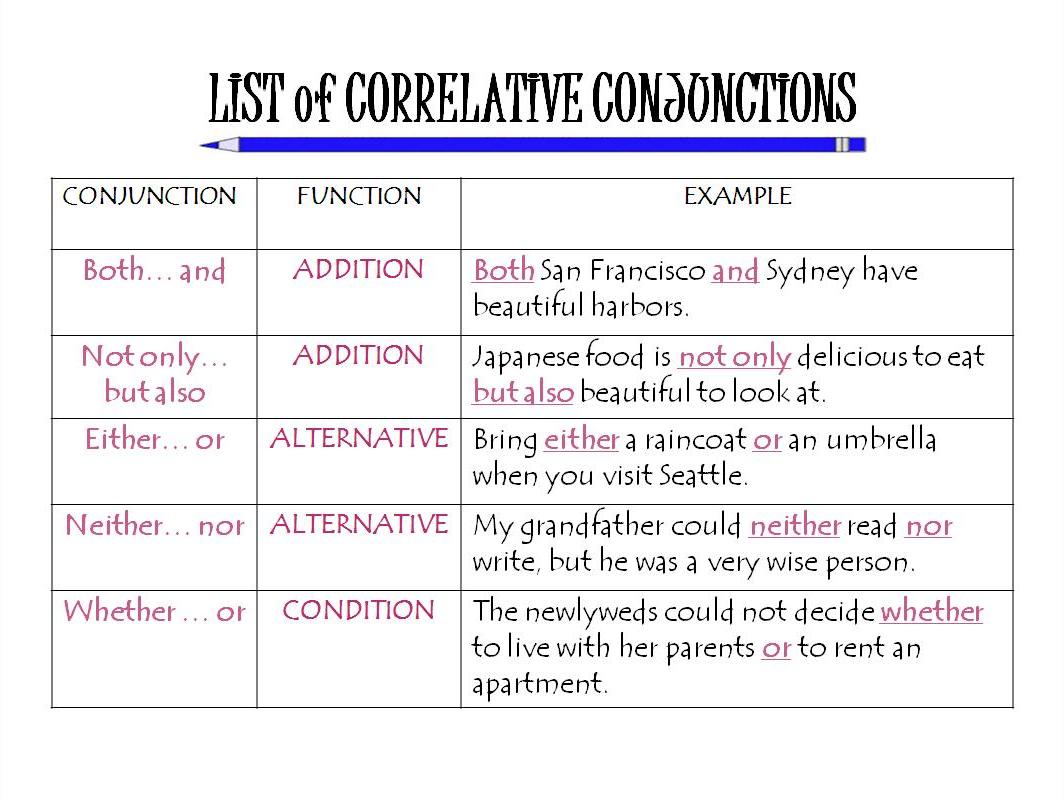
CONJUNCTIONS
SUBJECT-VERB AGREEMENT
NOUNS
ARTICLES
PRONOUNS
QUANTIFIERS